
Over the long term, it can cause contractures, sensory deficits, and paralysis.

Untreated compartment syndrome can lead to rhabdomyolysis, hyperkalemia, and infection. In addition to fractures, musculoskeletal injuries include Joint dislocations. Most fractures result from a single, significant force applied to normal bone. Risk is high with forearm fractures that involve both the radius and ulna, tibial plateau fractures (proximal tibial fractures that extend into the joint space), or tibial shaft fractures ( 1 Complications references A fracture is a break in a bone. Crush injuries or markedly comminuted fractures are a common cause, increasing tissue pressure as edema develops. read more : Tissue pressure increases in a closed fascial space, disrupting the vascular supply and reducing tissue perfusion. The earliest symptom is pain out of proportion to the severity of injury. doi: 10.1097/OI9.Compartment syndrome Compartment Syndrome Compartment syndrome is increased tissue pressure within a closed fascial space, resulting in tissue ischemia. Surgical timing for open fractures: Middle of the night or the light of day, which fractures, what time? OTA International: The Open Access Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma. Management of Gustilo–Anderson IIIB open tibial fractures in adults-a systematic review. For this reason, early treatment for an open fracture focuses on preventing infection at the site of the injury.
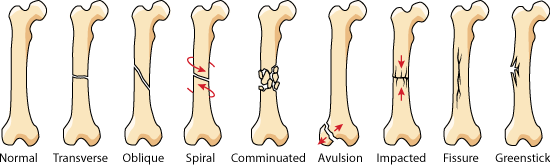
CLOSED FRACTURE VS OPEN FRACTURE SKIN
Once the skin is broken, bacteria from dirt and other contaminants can enter the wound and cause infection. Myatt A, Saleeb H, Robertson GAJ, Bourhill JK, Page PRJ, Wood AM. An open fracture requires different treatment than a closed fracture, in which there is no open wound. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research. Current concepts and ongoing research in the prevention and treatment of open fracture infections. Grade IIIC fractures specifically require vascular intervention, since the fracture is associated with vascular injury to the extremity.Grade IIIB fractures have significant soft-tissue damage or loss, such that bone is exposed, and reconstruction may require a soft-tissue transfer (flap) to be performed in order to cover the wound.Most surgeons classify high-energy fractures as IIIA even if the skin wound is not large. Grade IIIA fractures include high-energy fractures, as evidenced by severe bone injury (segmental or highly comminuted fractures) and/or large, often contaminated soft-tissue wounds.Grade III open fractures represent the most severe injuries and include three specific subtypes of injuries.Grade II fractures have larger soft-tissue injuries, measuring more than one centimeter.Sometimes it is difficult to assess if a fracture is open (meaning the wound connects to the broken bone), but this can be determined by injecting fluid into the fracture site and seeing if the fluid exits from the wound. A grade I open fracture occurs when there is a skin wound that communicates with the fracture measuring less than one centimeter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
